Difference between revisions of "CRTC I2M"
(→Example Dataset) |
(→Example Dataset) |
||
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
<pre>docker run -v $(pwd):/data/ cnf_tools tessellate --input ./CNF_SHARE/CFF_14052019/NT_140519.nrrd --delta 6 --output mesh0.vtk</pre> | <pre>docker run -v $(pwd):/data/ cnf_tools tessellate --input ./CNF_SHARE/CFF_14052019/NT_140519.nrrd --delta 6 --output mesh0.vtk</pre> | ||
| + | |||
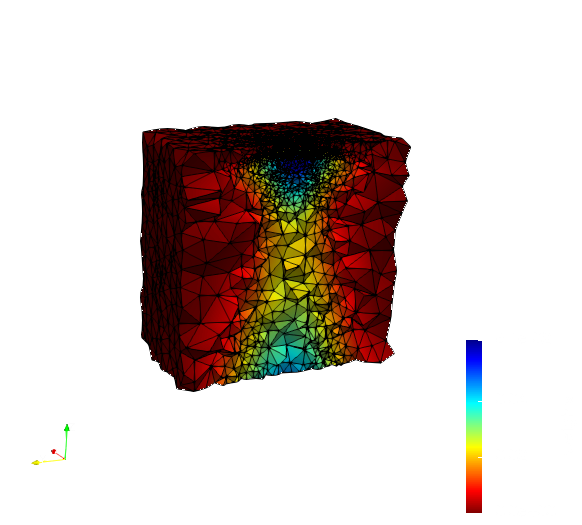
| + | For more examples see https://crtc.cs.odu.edu/CNF_Example_Meshes | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 19 November 2019
Contents
This page contains instructions for downloading and using the CNF_tools suite developed at CRTC lab in Old Dominion University in collaboration with Jefferson Lab.
This project corresponds to Proposal No.: CNF19-04 (FEMT-002)
A short presentation can be found here
The main component of the software suite is a 3D tessellation software called PODM capable of generating unstructured tetrahedral meshes out of 3D structured data.
The output meshes are in the VTK format and can be visualized using the opensource software Paraview. A short video demo exploring the data can be found here.
Requirements
- OS: Linux, Windows 10 Pro/Enterprise, MacOS Sierra 10.12+
- Docker
Installing Docker
Official documentation :
Note for Running on Windows
Docker on Windows uses Hyper-V VMs to run Linux containers. By default, the spawned VMs use 2 vCPUs and 2 GB RAM.
If performance is a concern, it is recommended to edit the Docker settings via the GUI to increase the resource allocation for the VMs in order to allow the tessellation tool (PODM) to to use more threads.
Getting the software
The docker image is located here (restricted access).
Docker Container Instructions
Load the Docker Image.
First of all, the Docker image needs to be loaded. The following command must be used:
docker load --input [DOCKER_IMAGE_TAR]
Note: If the user is not in the
dockergroup, prependingsudoto the above command is necessary.Running Currently the docker image includes three tools
tessellate2d,tessellate3dandconvert_imageTo use the tessellation tool use:
On MacOS/Linux
docker run -v $(pwd):/data/ cnf_tools <application> [arguments]
On Windows with Powershell (recommended)
docker run -v ${PWD}:/data/ cnf_tools <application> [arguments]On Windows with command line (cmd)
docker run -v %cd%:/data/ cnf_tools <application> [arguments]
Where <application> is one of the currently available tools : tessellate2d ,tessellate3d or convert_image.
Tessellation Parameters
A quick way to view all available parameters and brief descriptions for them is to pass the --help flag to tessellate2d/tessellate3d.
Below are more detailed descriptions of the tessellate parameters:
The common parameters for both versions are :
--input [filename] (required)
Input file (3D image). Can be in nrrd format.
--output [filename] (optional)
The filename of the output mesh. (default: outputMesh.vtk).
--weight-limit [real] (optional)
Set a weight limit for the generated elements that will be used from the sizing function (default: 0.1). This parameter acts as a limit for the relative difference of the weights for a sample of points within the element. It is designed to give some control on the discretization error with respect to the input data.
--min-edge [real] (optional)
Set the minimum edge size of generated elements that will be used for the sizing function (default: 1). It is designed to be used together with weight-limit controlling the size of the generated mesh.
Tessellate3D Specific Parameters
--delta [real] (required)
Controls the size of the elements nearby the boundary. Smaller values will lead to finer detail close to the boundary (and often to a more accurate mesh) but will also lead to a greater mesh size.
--threads [int] (optional)
How many threads to use. (default: 1)
--plc [filename] (optional)
If given, the surface of the produced mesh will be saved into filename in the VTK format.
--memory-limit [int in MB] (optional)
Constrain the amount of memory that will be used (default : 70% of the free memory).
--verbose-level [0,1,2] (optional)
Control the level of verbosity. 0 produces no text output while 2 enables extra information (default: 1).
--background-value [real] (optional)
Which voxel value to treat as background value. If none is desired, enter a value that does not exists in the dataset. (default: +∞). In practice, a background value is a value that is ignored from the tessellation procedure. Regions of the tessellation corresponding to the background value will have no elements.
--all-statistics (optional)
Output all statistics (thread and mesh).
--thread-statistics (optional)
Output thread statistics.
--mesh-statistics (optional)
Output mesh statistics.
Tessellate2D Specific Parameters
--verbose-level [0,1] (optional)
Control the level of verbosity. 0 produces no text output while 1 produces the standard amount of information (default: 1).
convert_image parameters
convert_image serves as a utility to convert input data between different kinds of image formats. For example the .nrrd images acquired from Jefferson lab cannot be used with Paraview in order to create contour-plots (unknown why). However, converting them using
docker run -v $(pwd):/data/ cnf_tools convert_image input_image.nrrd output_image.vtk
enables all relevant image filters in Paraview.
Example Dataset
Generated using :
docker run -v $(pwd):/data/ cnf_tools tessellate --input ./CNF_SHARE/CFF_14052019/NT_140519.nrrd --delta 6 --output mesh0.vtk
For more examples see https://crtc.cs.odu.edu/CNF_Example_Meshes